1. Light decay will affect the life of the LED
What is light luminous decay?
In daily use, we often find that LED lights become dimmer and dimmer. This phenomenon is the so-called LED light luminous decay phenomenon.
LED light luminous decay is the weakening of the signal in the transmission of light, and the light decay of LED products made by the world's largest LED manufacturers at this stage are different, high-power LEDs also have light decay, which is directly related to the temperature.
Light failure generally refers to its luminous flux, when charging the surface of the photoconductor drum, as the charge accumulates on the surface of the drum, the potential also rises, finally reaching the "saturation" potential, which is the highest potential. The surface potential decreases over time and is generally lower than this potential when working, a process that naturally decreases over time, called "dark decay". When the light-sensitive drum is scanned and exposed, the surface of the photoconductor is not exposed to light, i.e. the dim area where we see the potential is still in the dark decay process. This is called "light luminous decay".
The relationship between light luminous decay and the life of LED products.
Light degradation has a very significant impact on the life of LEDs, and the best way to reduce light degradation is to improve the efficiency of heat dissipation.
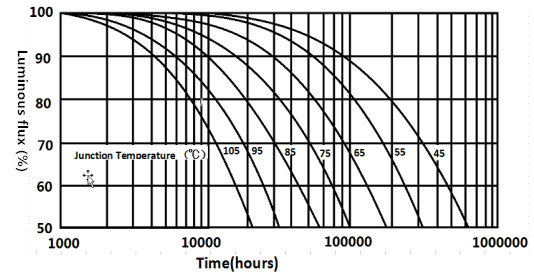
From the graph of a company's LED products light decay curve, we can see that LED light decay is related to its junction temperature. The so-called junction temperature is the temperature of the semiconductor PN junction, the higher the junction temperature the earlier the light decay, that is, the shorter the life. As can be seen from the graph, if the junction temperature is 105 degrees, the brightness drops to 70% of the life of only 10,000 hours, 95 degrees will have 20,000 hours, while the junction temperature is reduced to 75 degrees, the life of 50,000 hours, 65 degrees can be extended to 90,000 hours. So the key to a longer life is to reduce the junction temperature.
The key to reducing the junction temperature is to have a good radiator to dissipate the heat efficiently and in a timely manner. If we can measure the junction temperature achieved by any of the heat sinks, then not only can we compare the cooling effect of various heat sinks, but we can also know the LED life that can be achieved after using such heat sinks.
How to measure the temperature junction?
Once the heat sink has been installed, we find that it is not easy to measure the temperature of the heat sink, because usually the LED is welded to the aluminium substrate, which is mounted to the heat sink. If you can only measure the temperature of the heat sink housing, then to derive the junction temperature you must know the value of many thermal resistances. It contains the junction to the shell of the thermal resistance, the shell to the aluminium substrate, which in fact should also include the thermal resistance of the film printing plate, the thermal resistance of the aluminium substrate to the heat sink, the heat sink to the air thermal resistance. There are so many influencing factors, which as long as one of the data is not accurate will affect the accuracy of the test.
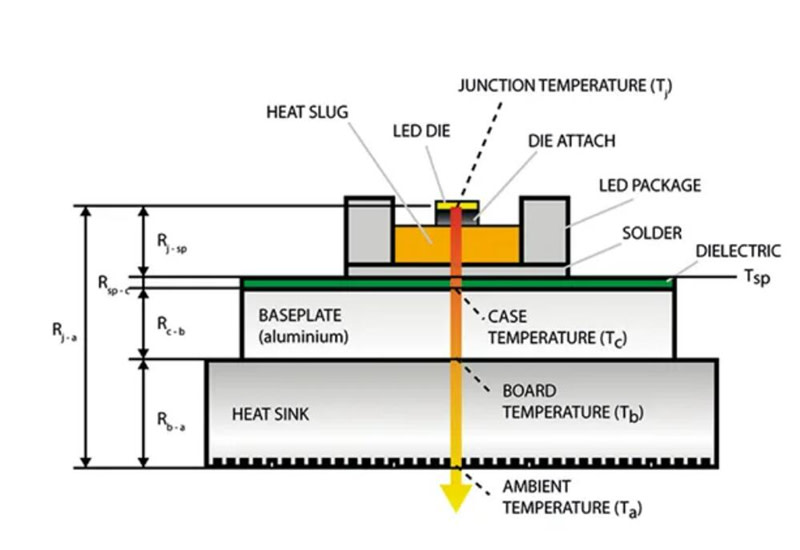
The diagram above gives a schematic view of the individual thermal resistances from the LED light source to the heat sink. As can be seen from the diagram there are many parts of the thermal resistance structure, making its accuracy even more limited. This means that it is even more difficult to deduce the accuracy of the junction temperature from the measured surface temperature of the heat sink.
The LED is a semiconductor diode which, like all diodes, has a voltammetric characteristic and, like all semiconductor diodes, this voltammetric characteristic has a temperature characteristic. The characteristic is that when the temperature rises, the voltammetric characteristic shifts to the left. This means that as the temperature changes, the volt-ampere curve shifts by a fixed temperature coefficient. As long as the temperature coefficient of the LED is known, it is easy to deduce the junction temperature of the LED from the measured forward voltage of the LED.
The calculation of the temperature coefficient is not developed in detail here. Professional LED suppliers have tables on the temperature coefficient of LEDs for reference. The buyer only needs to know that the higher the junction temperature, the earlier the light decay, i.e. the shorter the life span, to be able to judge the life span of the LEDs they purchase.
2. How to predict the life of LED lights
As can be seen from the light decay curve, the service life of LEDs is closely related to the junction temperature. Through the junction temperature can roughly determine the life of the LED lamp. For example, from the curve in Figure 1 can be seen from the junction temperature of 105 degrees, the life of only 10,000 hours, 95 degrees junction temperature life will have 20,000 hours, junction temperature reduced to 75 degrees, life will have 50,000 hours, as the junction temperature decreases, life is increasing trend.
Indoor LED lamps are less affected by the natural environment and their life is relatively stable, while for outdoor LED lamps, purchasers also need to consider natural environmental factors, such as the impact of sunlight on material ageing, the impact of dust, etc., which can cause uncertain changes in the heat dissipation effect.
This also requires the purchaser to consider whether the product design is friendly to heat dissipation when purchasing LED products. Previous articles have also mentioned related topics, such as the back cooling fins of floodlights, which require the largest possible surface area for heat dissipation.
In summary, the life of an LED is inextricably linked to its heat dissipation. When purchasing, purchasers can ask their suppliers for tables of relevant junction temperatures to understand the heat dissipation of their products. For purchasers who have obtained samples, they also need to pay special attention to the changes in product temperature during the testing process.
To obtain more information about this, please follow us on our official website https://www.hbsocket.com/.