LED lighting is becoming more and more widely used in life and heat dissipation is an important factor in the quality and life of LED lighting. Although the temperature rise of LED lighting is much less than that of traditional halogen lighting, many manufacturers are producing LED lighting with luminous efficacy and rapid light decay lower than expected, mainly due to unsatisfactory heat dissipation. Many manufacturers and R&D personnel continue to focus on how to improve the heat dissipation of high-power LED lighting while controlling costs.
The relationship between heat dissipation and the lifetime
When we talk about the life of an LED in a professional context, we do not mean that it burns up or cannot be lit, but generally, when the LED light output reaches 70%, we consider it to be the end of its life. LED (Light Emitting Diode) light source is a solid-state semiconductor equipment, which can convert electric energy into light energy, but at the same time, part of the electric energy will be converted into heat energy, leading to the phenomenon of heating when lamps are in use. LED is mainly composed of the bracket, silver glue, wafer, gold wire (copper wire), epoxy resin, which except bracket and epoxy resin, the damage of remaining three materials can directly lead to LED chip stop working, and too high a temperature, just are the nemesis of above three materials. Insufficient heat dissipation in a high-temperature environment will accelerate the light decay of LEDs, and the service life will be reduced. Heat dissipation affects the application of light sources, so LED lighting must have heat dissipation devices, and heat dissipation has become an objective parameter to evaluate the merits of lamps.
Elements to improve heat dissipation
Heat dissipation in the traditional sense is the so-called transfer of heat, and the elements of heat transfer contain three points: conduction, radiation and convection. The most commonly used in lamps is heat conduction, where heat is transferred from a location where the temperature is too high to a location where the temperature is low. Therefore, the thermal conductivity of different materials and the structure of the radiator may have an impact on the heat transfer effect.
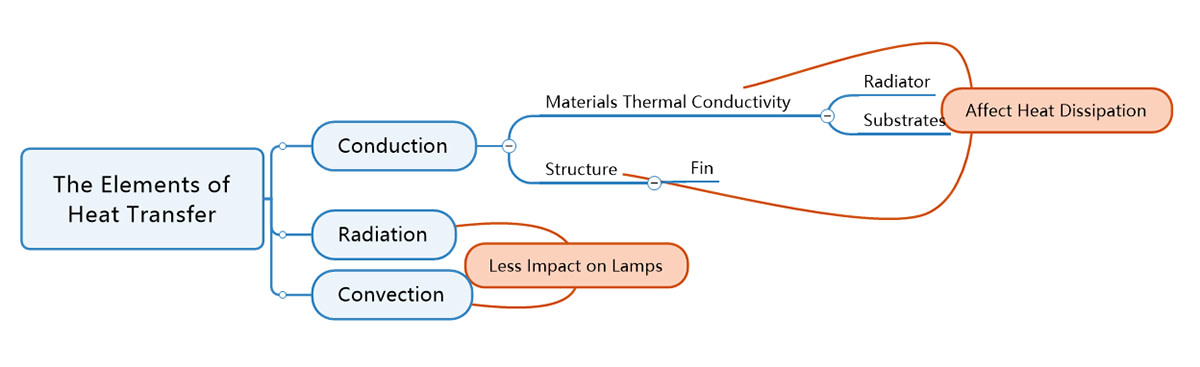
Heat dissipation materials
Among the various components of a lamp, the radiator and the substrate with the LED beads are the main dissipation methods. The different materials used for these two components can have a significant impact on the heat dissipation effect and cost.
Radiator
LED lighting radiator is generally made of aluminium, which is divided into two types, AL6060 and other aluminium-based stretch aluminium, ADC12-based die-casting aluminium. AL6060 and other stretches aluminium thermal conductivity is 198 ~ 250w/m ℃ or so, fast heat transfer, low mould cost and can be cut in any length, and the process is easy to produce processing, but its hardness is relatively low, and the appearance is not easy to change, and also difficult to make a more beautiful design. Although the thermal conductivity of ADC12 die-casting aluminium is only 96.7w/m ℃, the advantage is that the shape design can be made according to the aesthetic requirements of any shape you want, and the production efficiency is high. But its mould development cost is high, the development time is long, and it cannot be modified easily, generally used in the small size lighting, which does not need to modify the product, same it also occupies the radiator market for a long time because of its relatively cheap price.
Purchasers who are not very concerned about the appearance of the lamps and require price advantages can choose the AL6060 drawn aluminium style, while purchasers who require higher aesthetics of the product and will not change the design casually can be more partial to the die-cast aluminium style.
There are many large lighting manufacturers that have proposed the idea of plastic-coated aluminium material, which is a combination of the advantages of the two materials. It takes into account the poor thermal conductivity of plastic, but high insulation, easy mass production and low price, and the characteristics of metal aluminium that good heat dissipation but high cost. However, it is not yet widespread. Regarding to ordinary plastic-coated aluminium material, its heat dissipation effect is still not ideal. Because of the poor thermal conductivity of ordinary plastic, the heat inside the lamp is more difficult to export. If we use plastic-coated aluminium material, the effect is obvious, but it comes with the problem of complex production processes and high costs. For low-power lighting (below 10W), the use of ordinary plastic-coated aluminium is acceptable in view of the cost, but for high-power commercial lamps, die-cast aluminium is recommended.
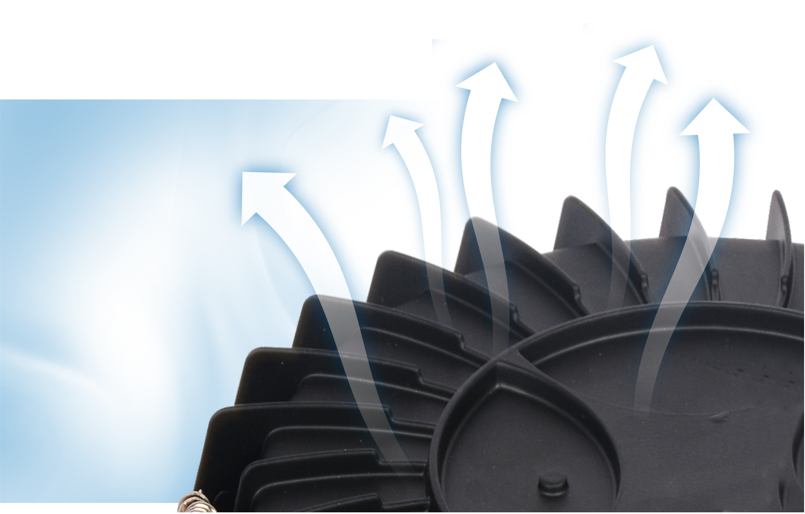

Substrates
In addition to the radiator, the substrate is also an important heat dissipation channel. The most common substrates available on the market for LED lighting are copper and aluminium. The thermal conductivity of copper substrates is better than aluminium substrates, but the price is relatively high. The market acceptance of aluminium substrates is higher, and most suppliers or designers will choose aluminium substrates as heat dissipation plates. Regarding to the quality, it depends mainly on the thickness of the aluminium plate, and a 0.8mm-2.0mm range is popular in the market. The thicker the better its thermal effect, and naturally price goes up. However, based on the price/performance ratio, a 1.0mm thick aluminium plate has a relatively good heat dissipation effect and the generally acceptable cost.
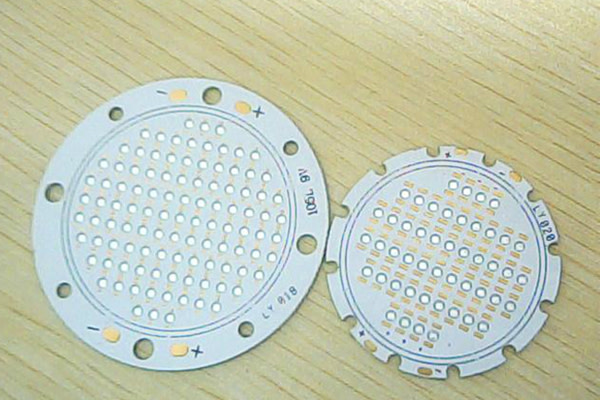


Heat dissipation Structure
The main structural influence on heat dissipation is the radiator. And as the structure of the substrate on the market tends to be more or less the same, its effect on heat dissipation can be negligible .
Radiators Design
Although aluminium is the best material to choose for the heat dissipation of lamps, most of the radiators on the back of lamps on the market are made of die-cast aluminium, but the price of raw aluminium is not cheap. Coupled with the impact of the epidemic, the price of aluminium raw material has climbed step by step. If you have to think about the most cost-effective heat dissipation improvement programme from aluminium, you can start by increasing its heat dissipation area.
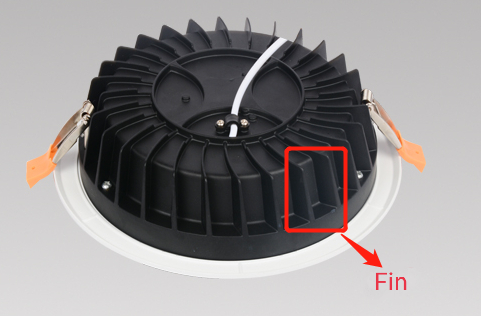
Radiators in LED lamps are generally designed with fins. The thickness of the radiator and thermal convection fins have a great impact on the heat dissipation efficiency. Regarding to qualified lamps, the thickness of the radiator can not be too thick nor too thin, and the distance between the fins as well as the thickness can not be too large or too small, which is to assess the professional level of a heat dissipation engineer.
In practice the required heat dissipation area for different power lamps can be calculated by using the heat exchange-convection formula [Q=Hc*A*(Tc-Ta)]. The designer can use this formula to optimise the simulation of the fin design to find the maximum heat dissipation area, and pay attention to the ratio of fin height to fin spacing, the ratio of fin height to fin thickness and the difference in width between the base and the end of the fins. In addition, the surface of the fins can be roughened or the side fins of the radiator can be increased to improve the effective surface area.
To optimise the performance of the LED lighting, it is an important step to select the need reached and most cost effective heat dissipation material, and to maximise the heat dissipation effect through improving the structure under cost control, by knowing the main heat dissipation components of the lamp, the heat dissipation effect of different materials and the structure of the radiator.